Slow network performance can be frustrating and hinder productivity, hence why being able to increase Network performance can have a significant impact on your overall experience.
Online gaming, movie streaming, file sharing, and seamless web browsing require an efficient and dependable network connection.
Buffering issues, slow download and upload rates, and frequent disconnections can all be caused by a slow network. It is essential to pinpoint the root causes of these issues and put workable remedies in place to enhance the efficiency of your network.
What is network performance optimization?
Network performance optimization refers to the practice of improving network efficiency and reliability.
To improve network performance, it is necessary to use strategies including updating network drivers, optimizing network settings, implementing QoS, removing bandwidth-hungry programs, and using network optimization tools.
What causes network performance issues?
Various factors can cause network performance issues. Here are some of the most common:
- Outdated or incompatible network drivers
- Incorrect network settings
- Apps hogging bandwidth
- Network congestion
- Wi-Fi signal limitations
- Bandwidth limitations from your ISP
- Suboptimal DNS settings
- Interference from other electronic devices
There are several methods and optimizations you may use to improve network performance. Let’s examine these methods.
1. Update the network drivers
For optimum performance, it’s essential to keep your network drivers updated. Slow speeds might be caused by outdated or unsuitable drivers, which can impede network performance.
To download the most recent network adapter drivers, visit the manufacturer’s website or utilize Windows Update.
Note: The steps presented below are general and will not be precisely the same on your OS.
1.1. Use Windows Update
- Click the Start button, and type Windows Update.
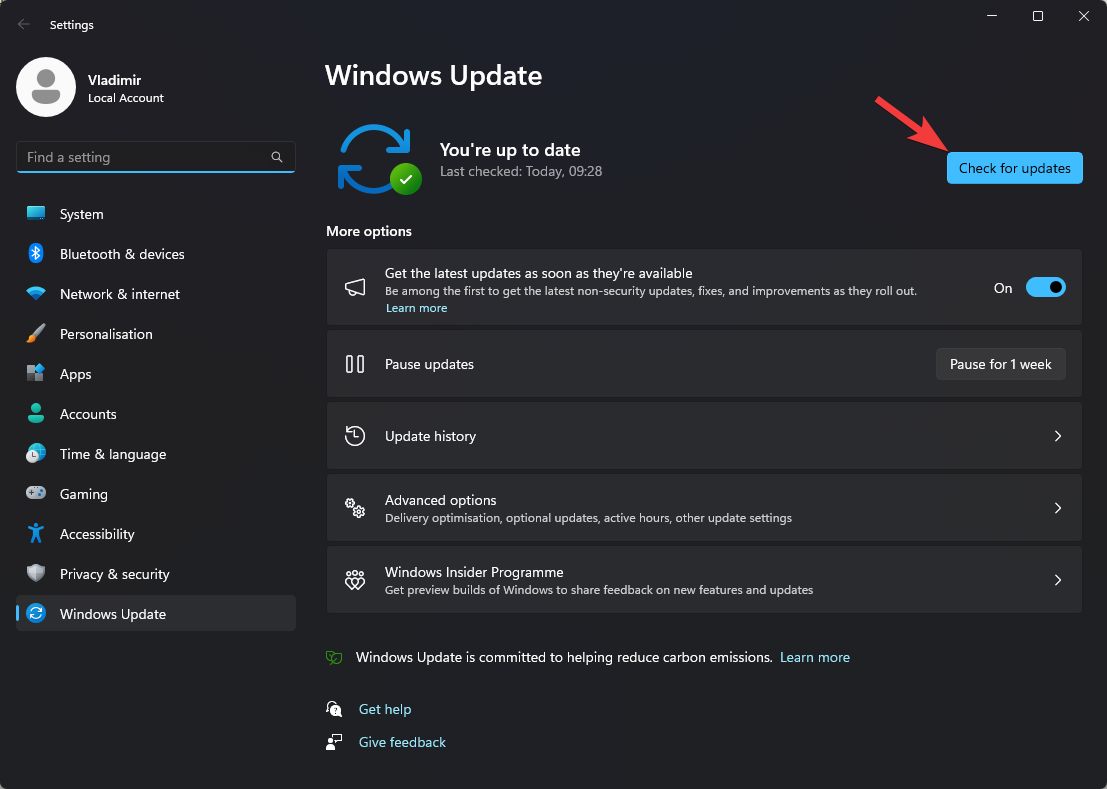
- Open the Windows Update app, and click Check for Updates.
- Install any updates and restart your PC if needed.
- After installing any Windows OS updates, follow the next method.
1.2. Use the Device Manager
- Press the Win + X keys on your keyboard.
- Choose Device Manager from the list that appears.
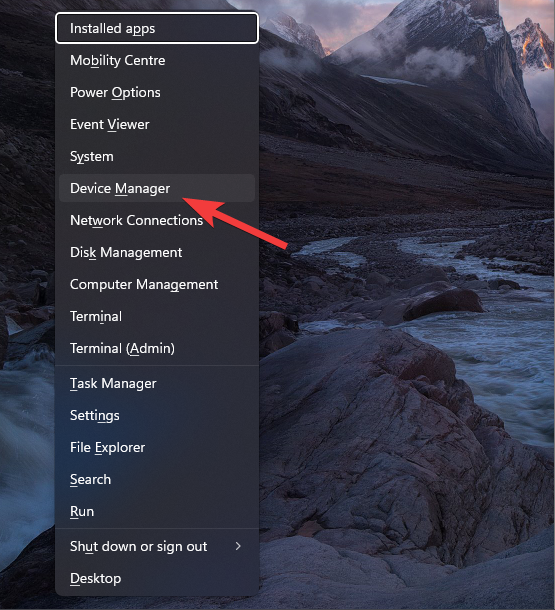
- Navigate to the Network adapter section inside the Device Manager.
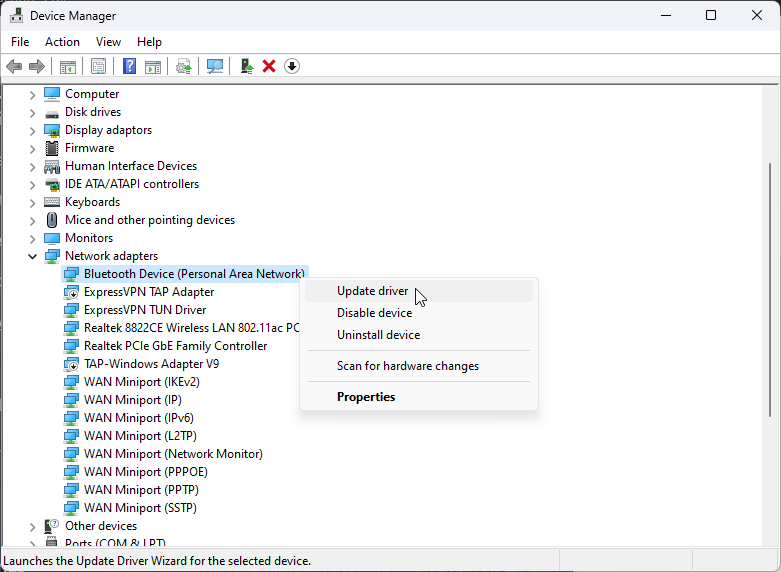
- Check for updated drivers, and install any if available.
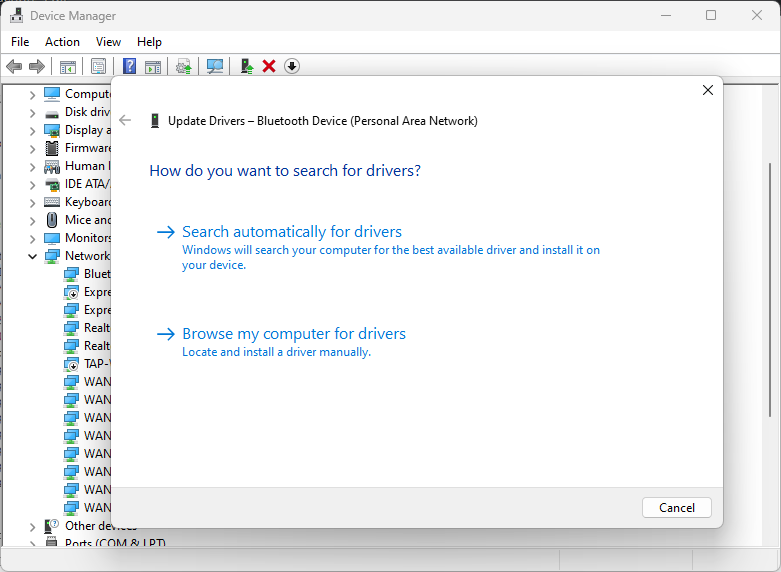
2. Activate Flow Control on your router/modem
When discussing network cards, the term flow control refers to a feature that aids in managing and regulating the flow of data packets in a network.
This acts as a mechanism for preventing packet loss and congestion by regulating the rate at which data is sent between devices.
The Flow Control feature usually is available in network switches, routers, and network interface cards (NICs).
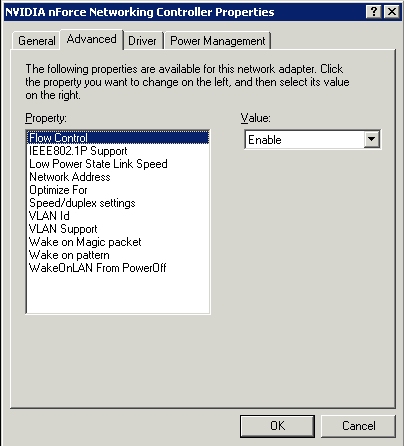
Here is how you can reach these settings:
- Find the make and model of your network card or switch/router by checking the device.
- Launch the web browser on a computer linked to the same network as the network card or router.
- Type your router’s IP address (found on the device or in the documentation), and press Enter to open the configuration interface.
- Enter the username and password (if you haven’t changed the default settings, then the information can be found in the documentation).
- Navigate to the network settings or advanced settings section.
- Look for the Flow Control option, which also might be labeled as IEEE 802.3x or Pause Frames.
- Enable the option, and configure it according to your network requirements
- Save the changes and exit the config page.
Note: Depending on your specific device, the actual process may differ from these general principles. For comprehensive instructions specific to your equipment model, refer to the manual or manufacturer’s website for your switch/router or network card.
3. Use Quality of Service (QoS)
By using quality of service, you can prioritize some network traffic over others.
You may ensure that essential operations like video conferencing or online gaming run smoothly by assigning bandwidth depending on particular apps or services.
3.1. Windows XP
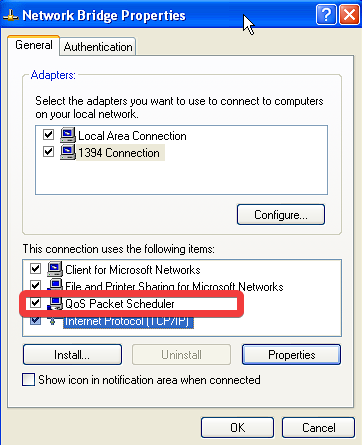
- Click Start and choose Control Panel, then double-click Network Connections.
- Right-click the network connection you want to modify and choose Properties.
- Click the QoS tab, and check the Enable QoS box on this interface.
- Configure the QoS to suit your network’s requirements.
3.2. Windows Vista and Windows 7
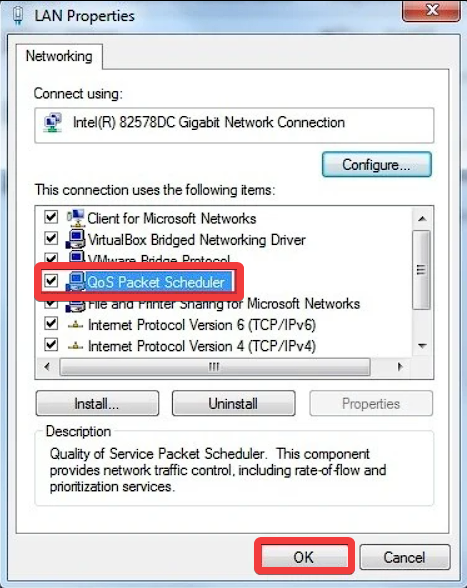
- Click Start and open the Control Panel.
- Choose the Network and Sharing Center option.
- Click the Change adapter settings option found on the left-hand side.
- Right-click the network you want to edit, and choose Properties.
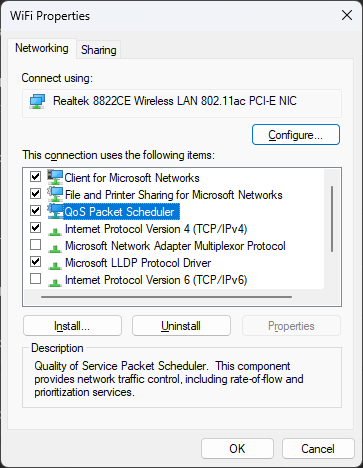
- Choose the Networking tab, and click on the QoS Packet Scheduler checkbox to enable it.
- Configure the QoS according to your needs.
3.3. Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Right-click the Start button and choose Settings.
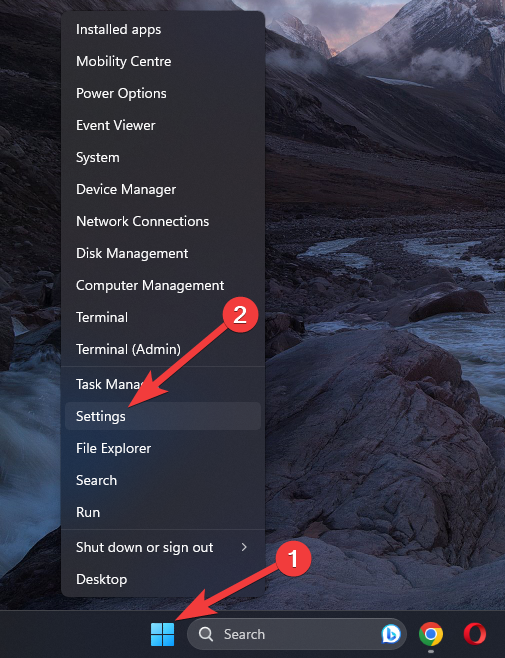
- Open Network & Internet, and click Ethernet or Wi-Fi, depending on your connection.
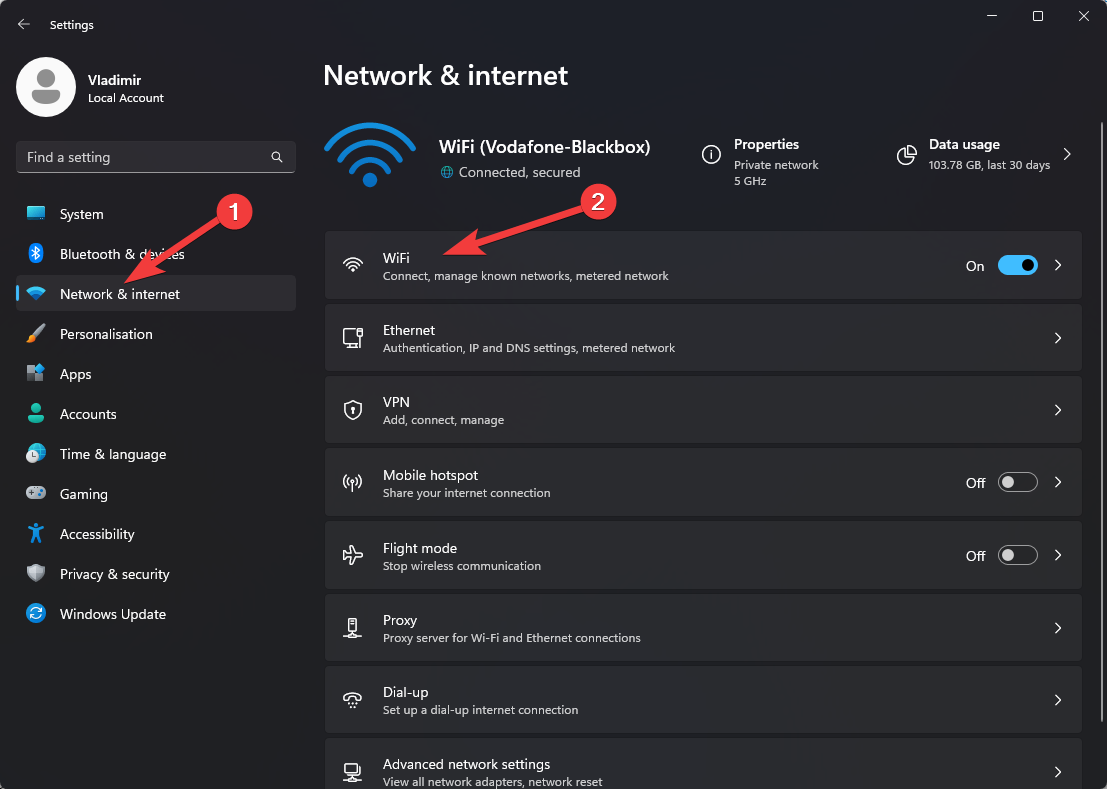
- Scroll down and choose Change adapter options or Advanced Network Settings.
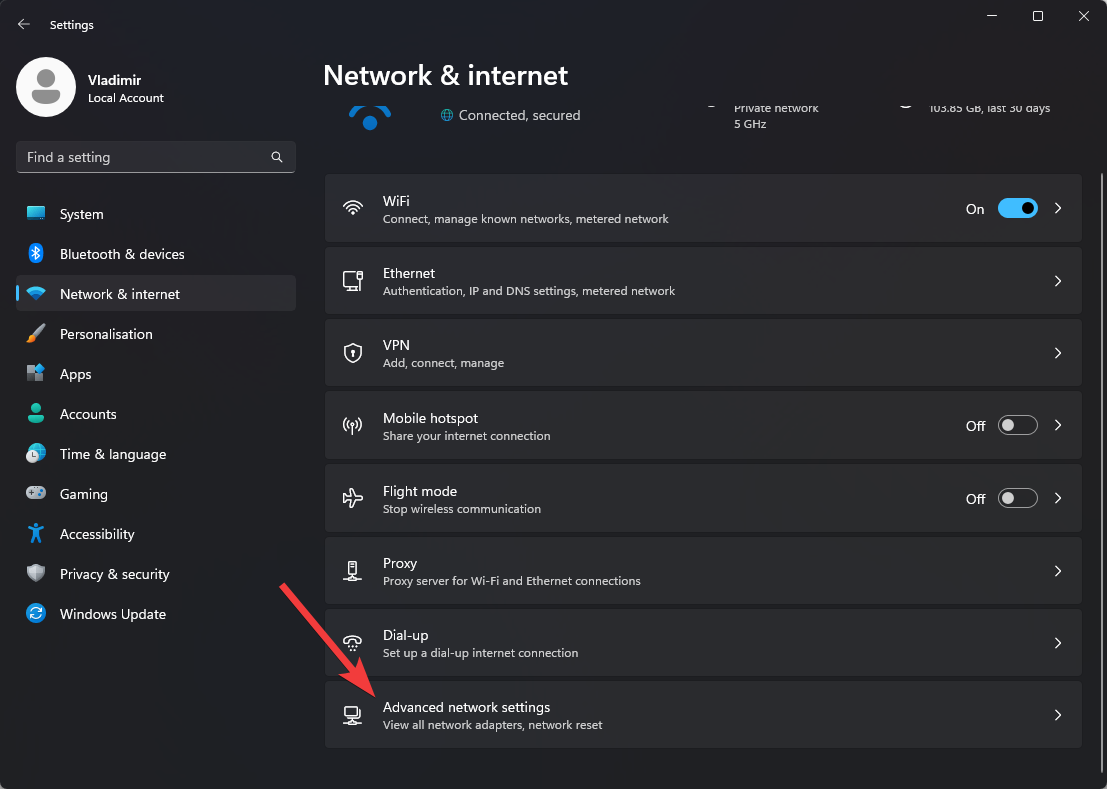
- Toggle the drop-down menu for the network connection you want to modify and choose Edit next to the More Adapter options section.
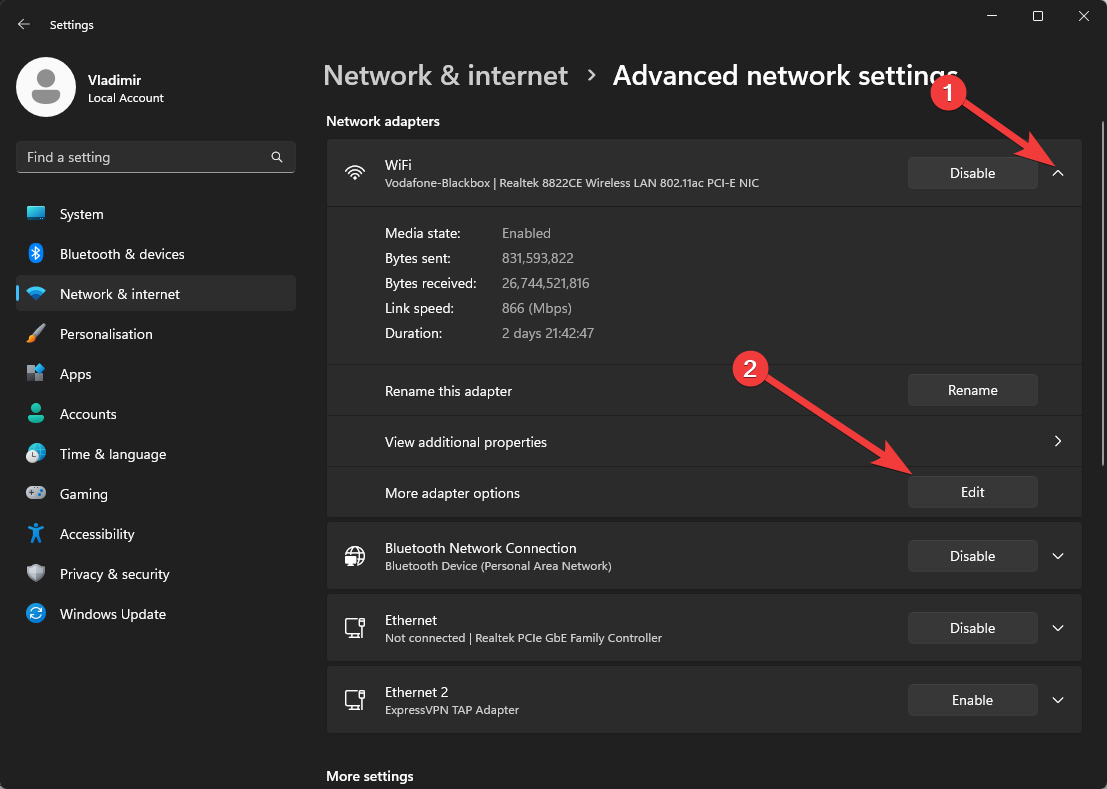
- Enable the option by checking the box next to QoS Packet Scheduler.
- Configure your network according to your desires.
4. Reduce the number of bandwidth-hogging apps
Some applications use an excessive amount of network bandwidth, which causes slower connection speeds for other tasks.
Locate and shut off applications that consume a lot of bandwidth, or modify their settings to lessen their effect on your network’s efficiency.
4.1. Windows XP, Vista, 7 and 10
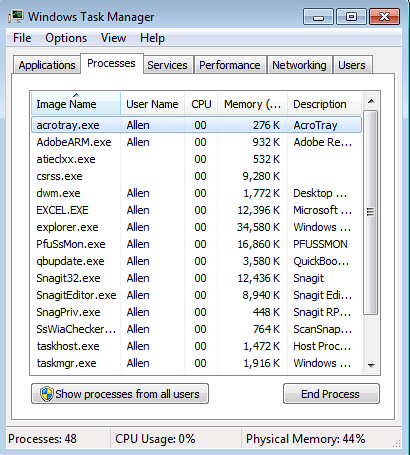
- Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc key combination to open the Task Manager.
- Click the Processes or Details tab, depending on your OS.
- Check for any apps that are using excessive bandwidth.
- Right-click the respective app, and choose End Process or End Task.
Note: It’s not advised to terminate an application or process if it’s a system process or essential to the operation of your system. Instead, you could change its settings or restrict access to the network.
You can try third-party software like NetLimiter, cFosSpeed, or Traffic Shaper XP to restrict an application’s access to the network. These tools will enable you to specify bandwidth restrictions for particular applications.
4.2. Windows 11
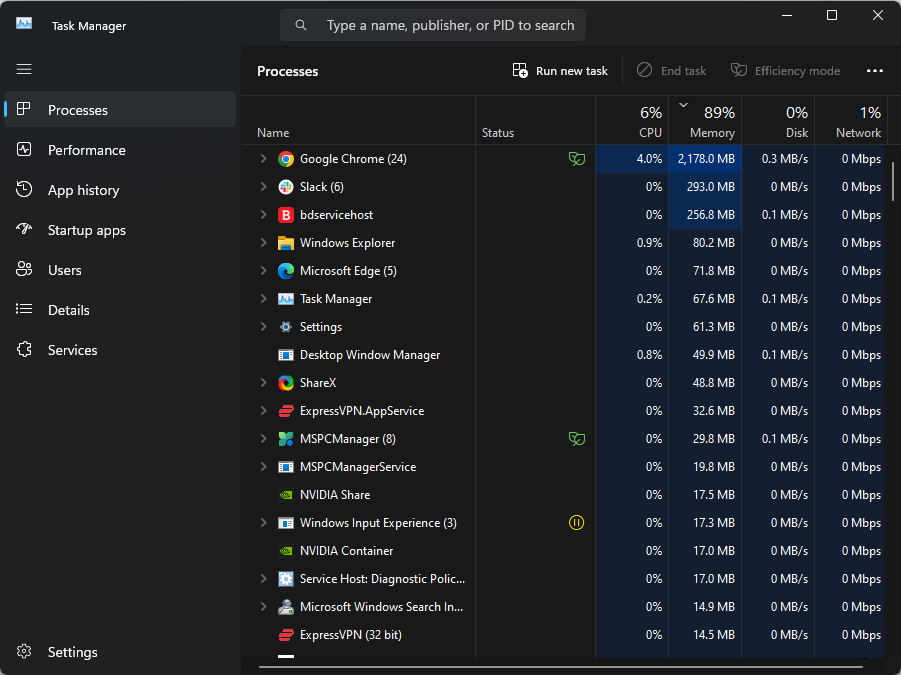
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys to open the Task Manager and choose the Processes tab.
- Find the app or process consuming too much bandwidth, right-click it, and choose End Task.
Note: Always exercise caution when closing processes or limiting network access because doing so can impair the application’s or your system’s functionality or performance.
Using the built-in Windows 11 feature known as Network Usage settings, you can restrict an application’s access to the network.
Here are the steps:
- Click the Start button and open the Settings app.
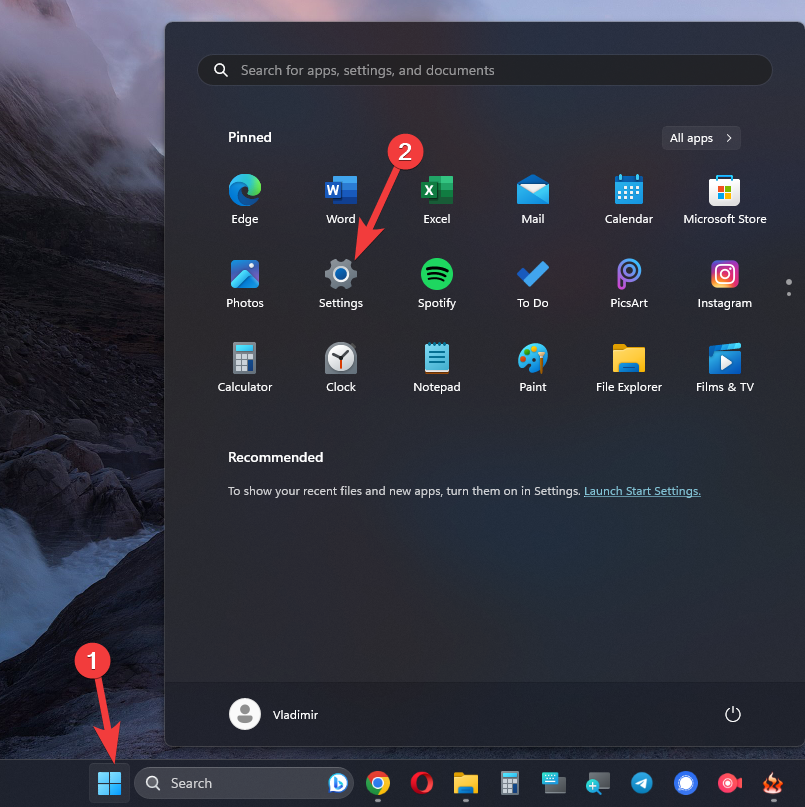
- Choose Network & Internet, and open the Advanced Network Settings option.
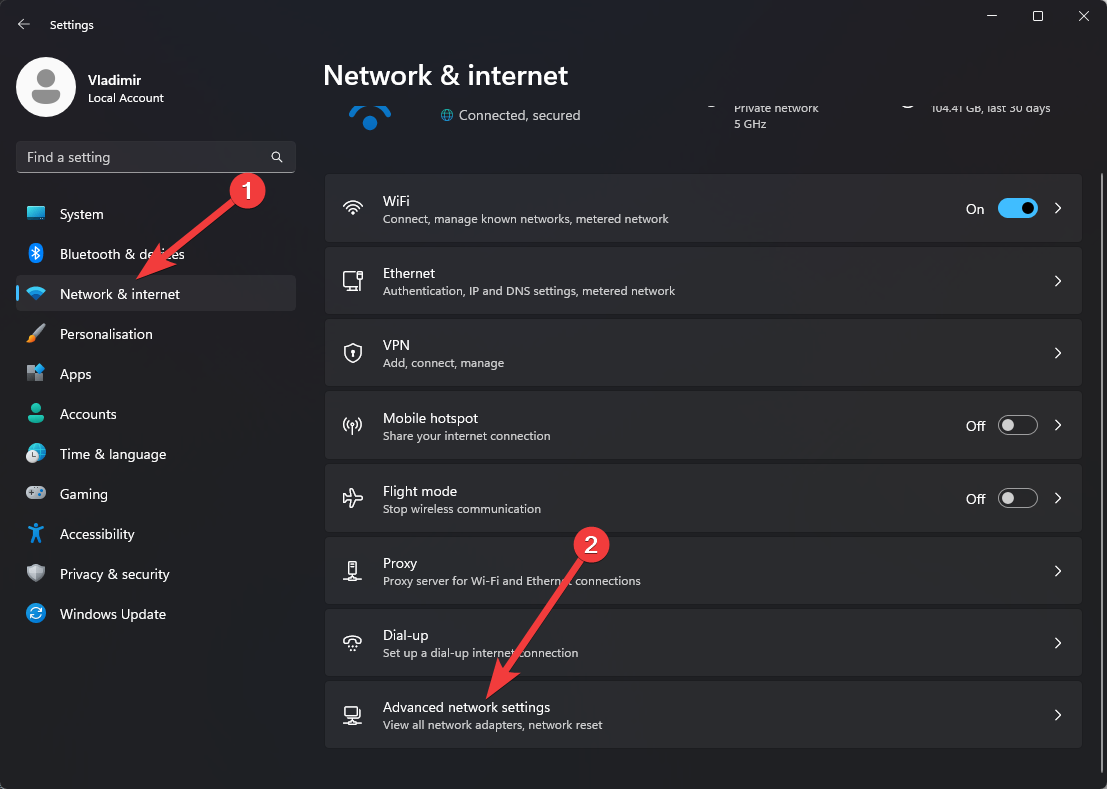
- Choose Windows Firewall from the list of options, and choose Advanced Settings.
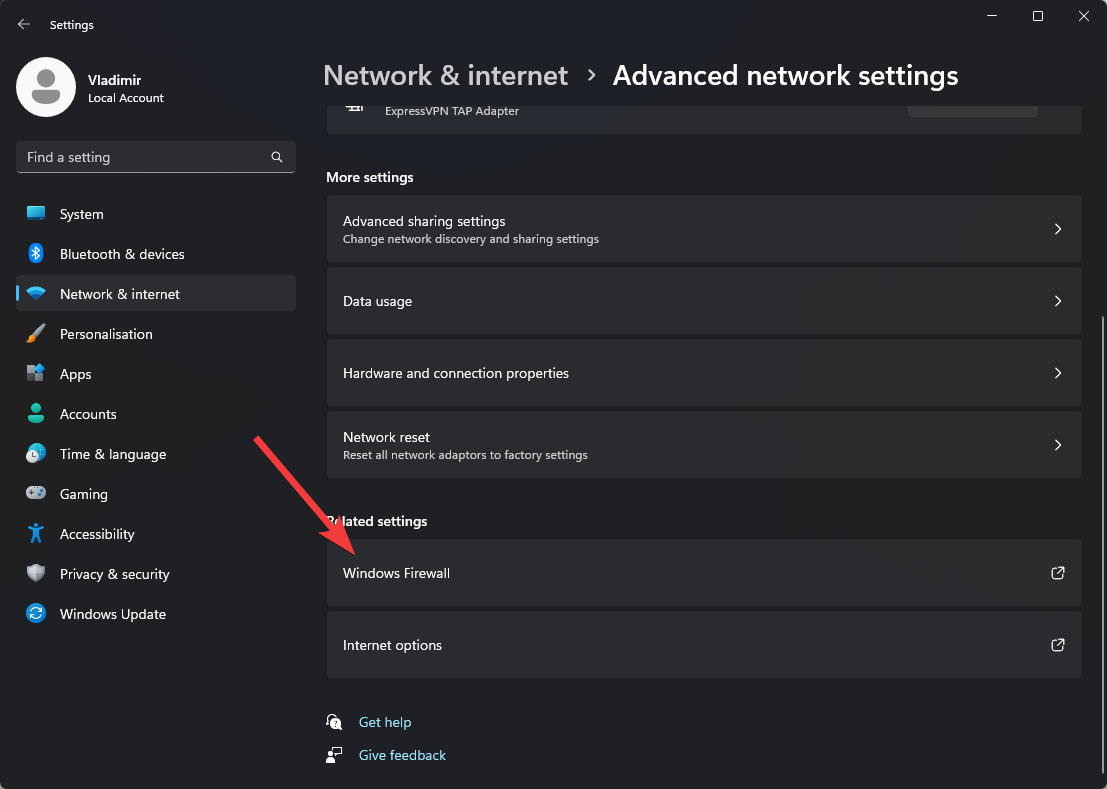
- Choose the Outbound Rules option from the left sidebar, and select New Rule from the right sidebar.
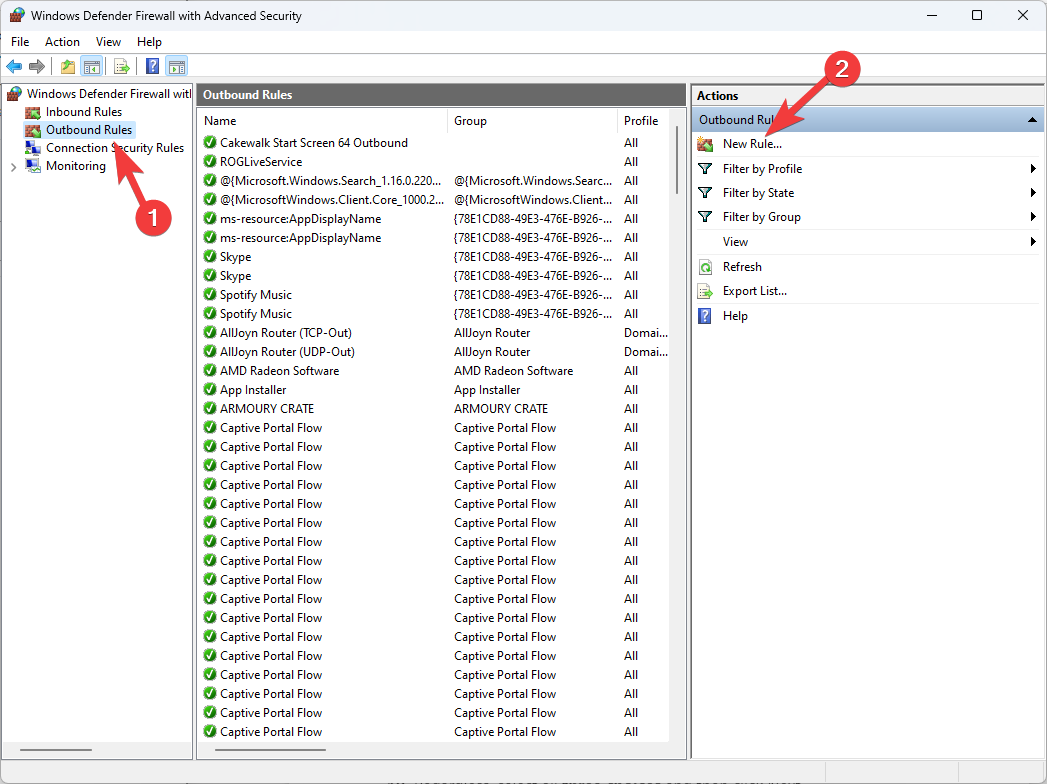
- Choose Program and click Next.
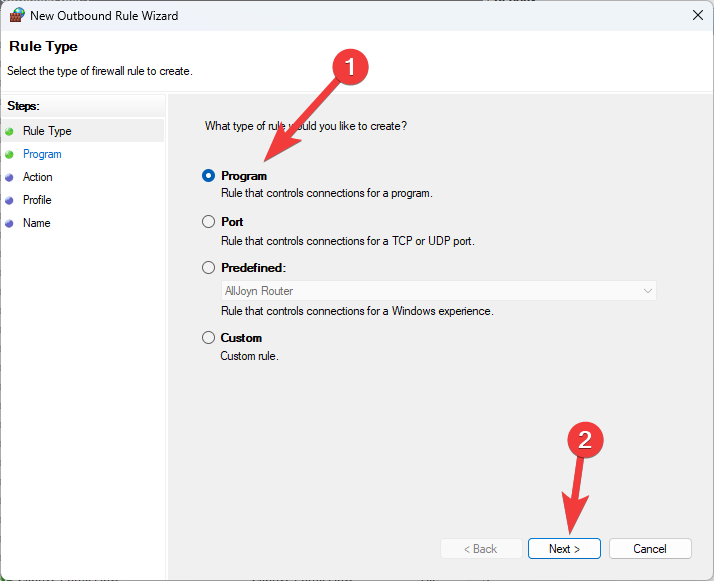
- Browse to the location of the app, and click Next.
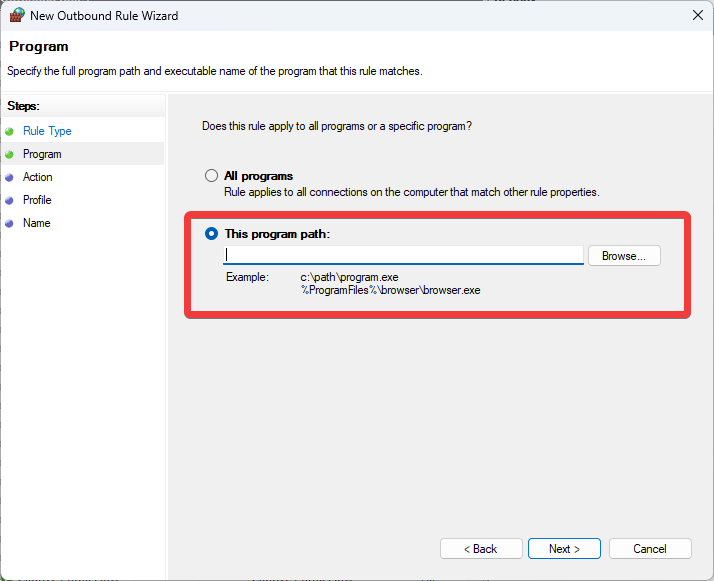
- Choose the Block the connection option and click Next.
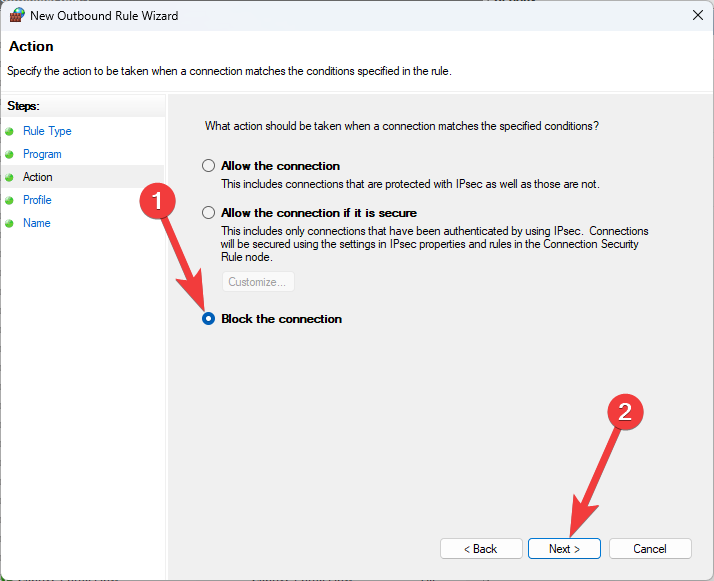
- Complete the setup process by adding the required information.
5. Disable the Auto-Tuning option
5.1. Windows XP
- Click the Start button and choose Run.
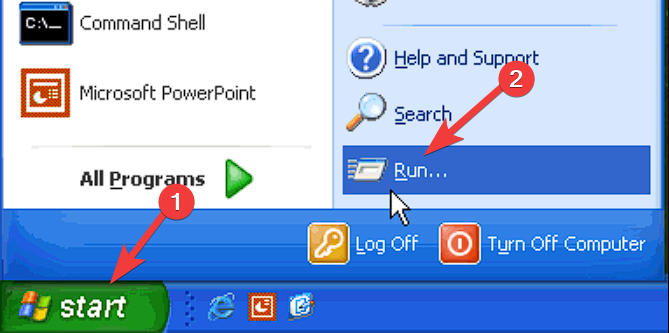
- Type cmd and press Enter to run the Command Prompt.
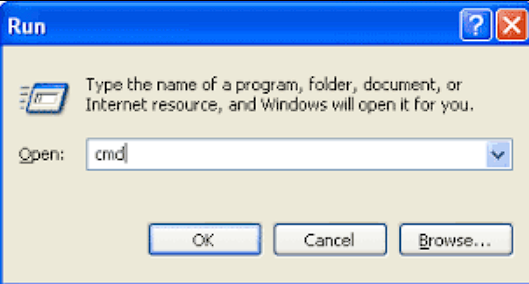
- Type the following command and press Enter:
netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled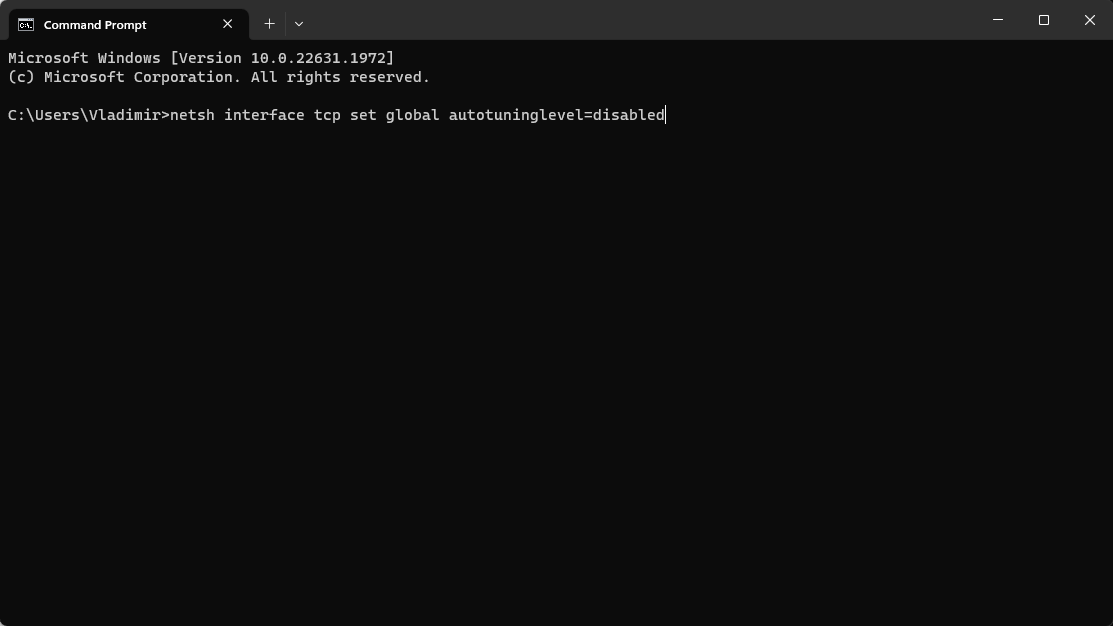
- Wait for the process to complete. The Auto-tuning feature will now be disabled.
5.2. Windows Vista and Windows 7
- Click Start, type cmd in the search box, right-click on Command Prompt, and choose Run as administrator.
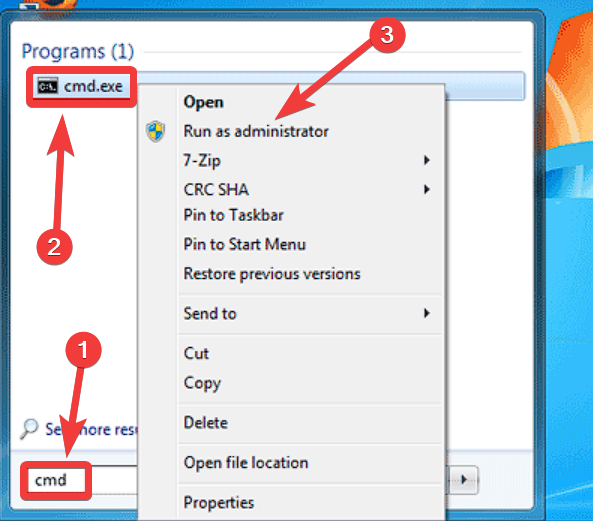
- Type the following command and run it by pressing the Enter key:
netsh interface tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled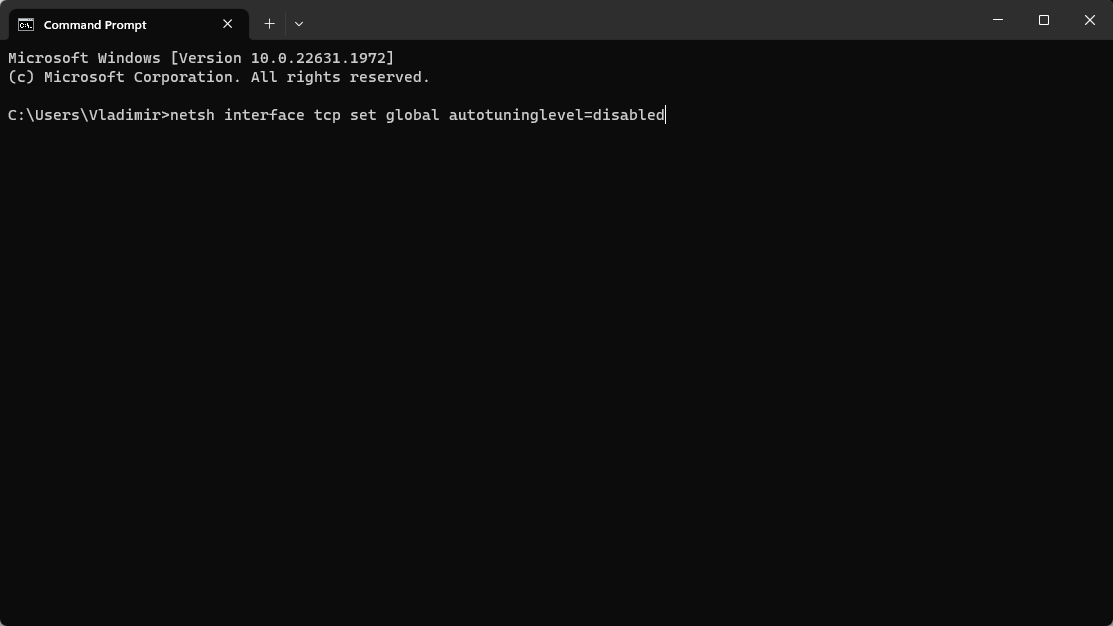
- This feature will now be disabled on your OS.
5.3. Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Right-click the Start button, and choose Windows PowerShell (Admin), Command Prompt (Admin), or Terminal (Admin), depending on the exact OS version.
- Type this command and press Enter to run it:
netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled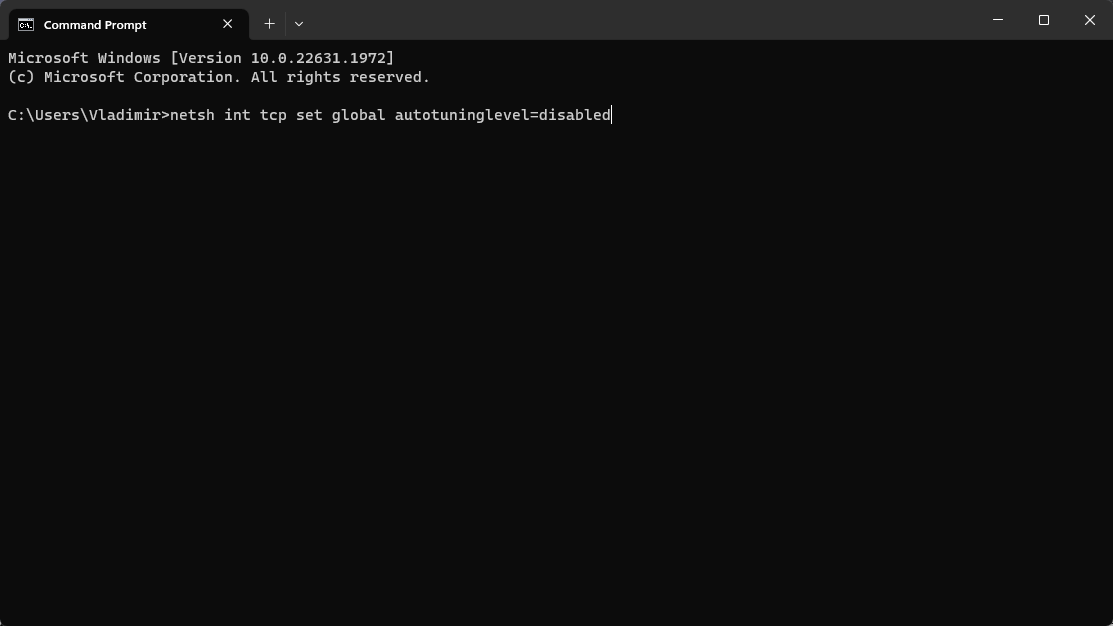
- The feature will now be disabled as soon as the process completes.
The Auto-Tuning feature on your Windows system will be disabled when you perform these steps. In some cases, especially in specific network setups, disabling Auto-Tuning can help increase network performance.
It’s vital to remember that this might not be required or advantageous for all network configurations, and its effects on performance might differ.
If you run into any problems after turning off Auto-Tuning, you can turn it back on by following the same procedures, just swapping out disabled for normal in the command:
netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=normal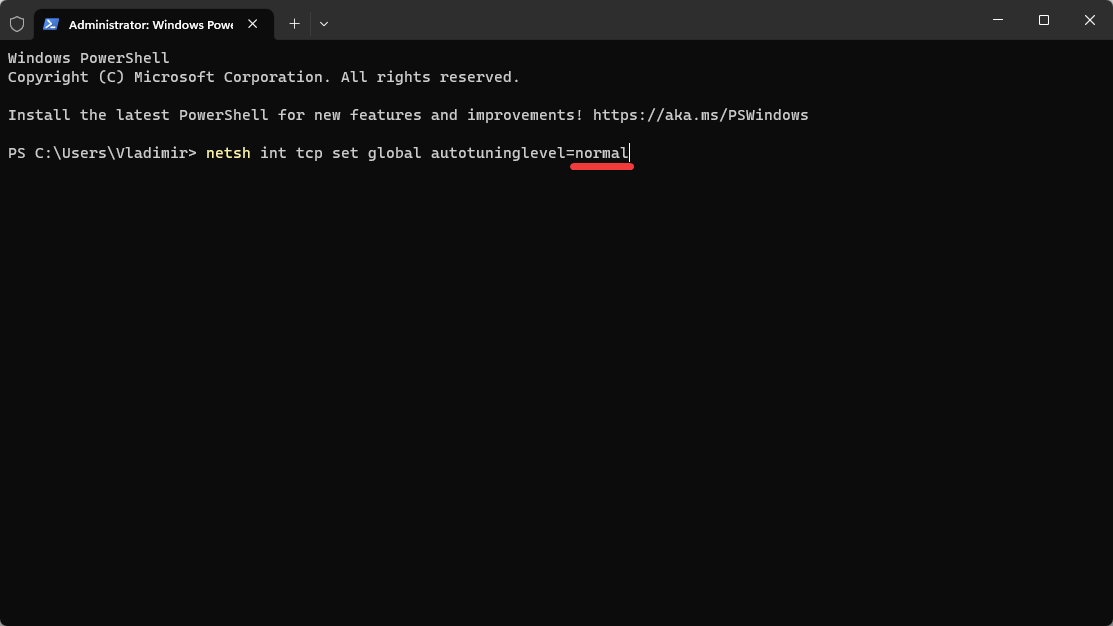
6. Optimize DNS settings
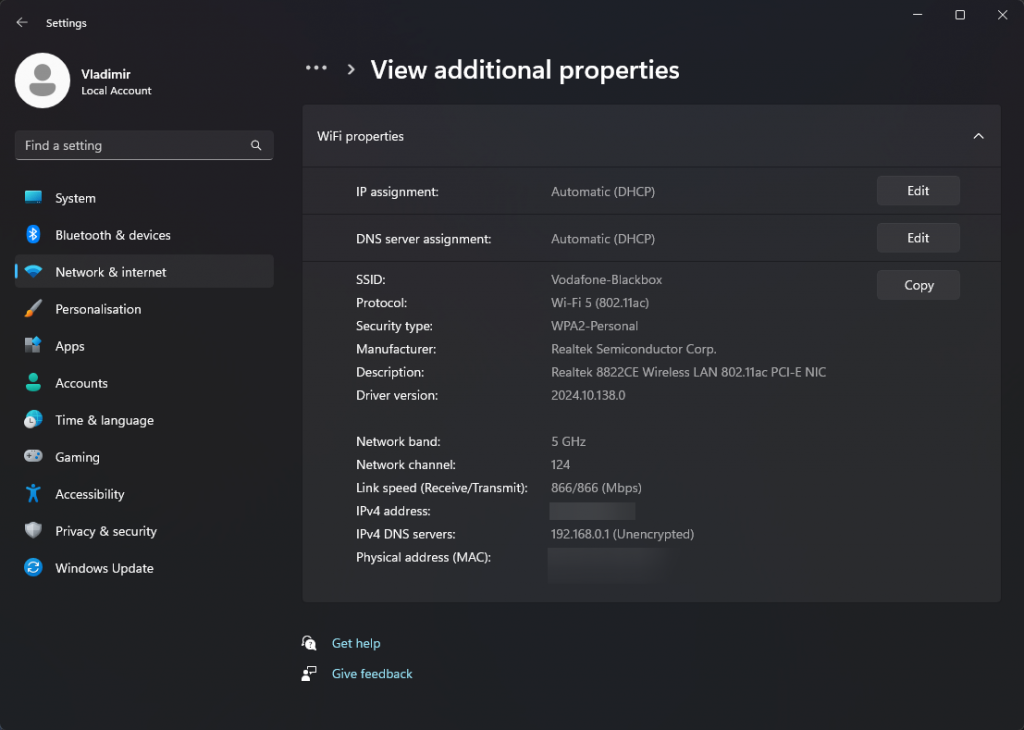
Domain names are converted into IP addresses by the Domain Name System (DNS).
You can speed up network responsiveness and decrease the time it takes to identify website addresses by using a dependable and quick DNS server.
Consider utilizing public DNS servers like Cloudflare DNS or Google DNS.
7. Disable the Remote Differential Compression option (Windows Vista and 7)
In some circumstances, disabling Remote Differential Compression might be helpful, mainly when dealing with poor network connections or problems with file transfer rates on Windows Vista or 7.
It’s crucial to remember that this function is intended to increase the effectiveness of file synchronization and might be advantageous in certain circumstances.
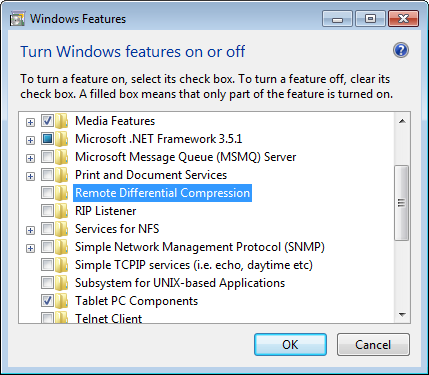
- Click Start and open Control Panel.
- Select the Programs option, and choose Programs and Features.
- Click the Turn Windows features on or off option from the left side panel.
- Scroll down and uncheck the box next to the Remote Differential Compression entry.
- Click OK to save the changes.
A reliable network is necessary for a seamless internet experience. You may enhance network dependability and maximize performance on Windows XP, Vista, 7, 10, and Windows 11 by implementing the strategies and using the technologies discussed in this article.
To monitor and improve the performance of your network, maintain your network drivers up to date, change network settings, use Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize traffic, and use tools like network analyzers, bandwidth monitors, and traffic shapers.

Vladimir Popescu
Verified at:
07/03/2023 10:31
Vladimir started writing articles about Windows because he has a natural interest in this topic, and he has been an avid professional user with more than 15 years of experience. He’s also been writing for WindowsReport.com, MSPoweruser.com and present in various other online publications on matters related to Windows and Windows servers.
Vladimir enjoys practicing Crossfit and making art when he’s not creating top articles with in-depth information.


Leave a Reply